Belly fat: Health risks & Lifestyle changes
Belly fat: Visceral fat that gathers around the stomach is the type known as belly fat. It is also known as abdominal or central obesity. Belly fat can be harmful to health as it increases the risk of various diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
There are many factors that contribute to the accumulation of Visceral fat, including genetics, lifestyle choices such as diet and physical activity, stress, and hormonal changes. To reduce Visceral fat, a combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can be helpful. It’s important to note that spot reduction of fat in a specific area, such as the belly, is not possible. Instead, a comprehensive approach to weight loss and fat reduction is necessary, which includes lifestyle changes that promote overall health and well-being.
What causes belly fat?
There are several causes that might contribute to Visceral fat, including:
- Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing Visceral fat due to their genetic makeup.
- Poor diet: A diet that is high in calories, sugar, and unhealthy fats can lead to the accumulation of belly fat.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of belly fat.
- Age: As we age, our metabolism slows down and we may start to lose muscle mass, which can lead to an increase in Visceral fat.
- Hormonal changes: Changes in hormones, such as those that occur during menopause or in men with low testosterone levels, can lead to an increase in belly fat.
- Stress: When we are stressed, the body produces cortisol, a hormone that can lead to increased fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area.
- Lack of sleep: Poor sleep quality or not getting enough sleep can lead to an increase in Visceral fat.
- Alcohol consumption: Abnormally high alcohol intake may be a factor in the development of abdominal fat.
It’s important to note that belly fat is often caused by a combination of these factors, and that everyone’s individual circumstances are different.
Health risks associated with belly fat
Belly fat is not just a cosmetic concern, as it has been linked to a number of health risks, including:
- Type 2 diabetes: Belly fat can cause the body to become resistant to insulin. Which can lead to high blood sugar levels and eventually type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular disease: Belly fat has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes.
- High blood pressure: Visceral fat can contribute to high blood pressure, which can further increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Sleep apnea: Excess Visceral fat can increase the risk of sleep apnea, a condition in which breathing is interrupted during sleep.
- Fatty liver disease: Visceral fat can contribute to the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Which can lead to liver damage and other health problems.
- Certain cancers: Belly fat has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, including breast and colorectal cancer.
It’s important to note that the health risks associated with Visceral fat can vary depending on factors such as age, gender, and overall health status. However, reducing Visceral fat through diet and exercise can help to reduce the risk of these health problems.
Also Read – Calf pain: Prevention & Treatment
How to reduce belly fat?
A mix of good eating practises, consistent exercise, and lifestyle adjustments are needed to reduce belly fat. The following advice may be helpful:
- Eat a healthy diet: Focus on eating whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats. Steer clear of processed meals, sweet beverages, and foods heavy in trans and saturated fats.
- Reduce calorie intake: In order to lose belly fat, you need to consume fewer calories than you burn. Tracking your calorie intake using a food diary or mobile app can be helpful in reducing overall calorie intake.
- Increase physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass, which can increase metabolism and burn more calories.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to reduce the production of cortisol, a hormone that can lead to increased Visceral fat.
- Get enough sleep: Attempt to get 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night. Lack of sleep can contribute to increased appetite and fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Alcohol is high in calories and can contribute to increased Visceral fat. Limit or completely avoid drinking alcohol.
- Consider a Mediterranean-style diet: This type of diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and healthy fats, and has been linked to reductions in belly fat and other health benefits.
It’s important to note that reducing belly fat takes time and effort, and it’s important to make sustainable lifestyle changes in order to maintain long-term success. Creating a specialised strategy to lose Visceral fat may also benefit from consultation with a trained nutritionist or medical specialist.
Foods that can help reduce belly fat
Certain foods can be beneficial in reducing belly fat when incorporated into a healthy, balanced diet. Here are some examples:
- Fiber-rich foods: Eating foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help reduce Visceral fat by keeping you feeling full and satisfied for longer periods of time.
- Lean protein sources: Eating protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and tofu, can help reduce belly fat by increasing metabolism and helping to build muscle mass.
- Healthy fats: Foods that are high in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, can help reduce Visceral fat by promoting feelings of fullness and improving heart health.
- Low-fat dairy products: Low-fat dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, can help reduce belly fat by providing calcium. Which has been shown to reduce belly fat and promote weight loss.
- Spices: Certain spices, such as turmeric, ginger, and cayenne pepper, can help reduce inflammation in the body. Which can contribute to the accumulation of Visceral fat.
- Green tea: Drinking green tea regularly has been shown to reduce Visceral fat by increasing metabolism and promoting fat oxidation.
It’s important to note that while these foods can be beneficial in reducing Visceral fat. They should be incorporated into a healthy, balanced diet that includes a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods.
Lifestyle changes to reduce belly fat
In addition to healthy eating habits and regular exercise, making certain lifestyle changes can also be helpful in reducing belly fat. Here are some examples:
- Reduce stress: Belly fat might build up as a result of ongoing stress. Exercises that reduce stress include yoga, meditation, and deep breathing.
- Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism. Which can contribute to increased belly fat. Make an effort to obtain 7-9 hours of sound sleep every night.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Alcohol is high in calories and can contribute to increased belly fat. Limit or completely avoid drinking alcohol.
- Quit smoking: Smoking has been linked to increased belly fat and a number of health problems. Quitting smoking can lead to improvements in overall health and reductions in belly fat.
- Reduce processed foods and sugar intake: Processed foods and foods high in added sugars can contribute to weight gain and increased belly fat. Limit your intake of these types of foods and focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods instead.
- Stand up more: Sitting for extended periods of time can contribute to the accumulation of belly fat. Try to stand up and move around every hour or so throughout the day.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help reduce belly fat by promoting feelings of fullness and improving metabolism.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine can help reduce belly fat and improve overall health.
When to seek medical advice
While making lifestyle changes such as healthy eating and regular exercise can be helpful in reducing belly fat, there may be cases where medical advice is necessary. Here are some scenarios when you might want to think about getting medical advice:
- If you have underlying health conditions: Certain medical conditions such as hypothyroidism, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or Cushing’s syndrome can contribute to increased belly fat. If you have any underlying health conditions. It’s important to work with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions and develop a plan to reduce belly fat.
- You’ve tried to modify your way of life, but haven’t had success: If you have been making healthy lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, but are not seeing improvements in your belly fat. It may be helpful to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian for further guidance.
- If your abdominal fat is very substantial: If you have a large amount of belly fat or if your waist circumference is significantly above the recommended range. It may be helpful to consult with a healthcare provider to assess your risk for health complications and develop a plan to reduce belly fat.
- If you are experiencing other health problems: If you are experiencing other health problems such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or type 2 diabetes. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to manage these conditions and develop a plan to reduce belly fat.
It’s important to remember that everyone has a different body, so what works for one person might not work for another. If you have any concerns about your belly fat or overall health. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider.
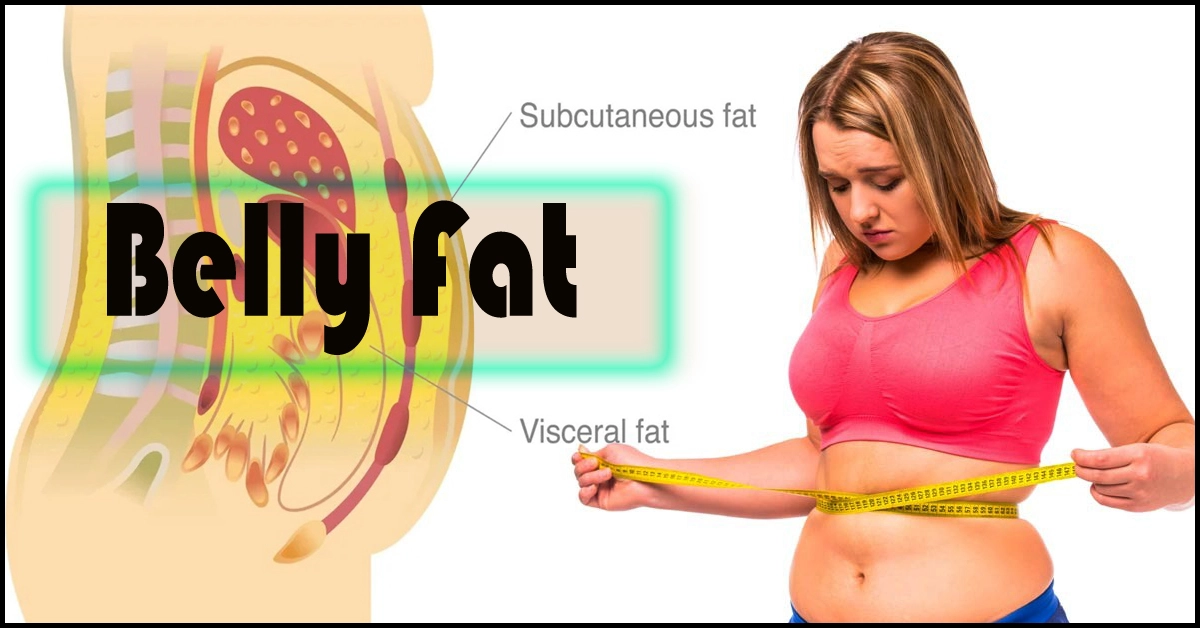
Different types of belly fat
Two basic categories of abdominal fat exist:
- Subcutaneous fat: This is the fat that is located directly under the skin and is the type of fat that is typically visible as a belly “pooch”. While subcutaneous fat can contribute to an increase in waist circumference. It is not as harmful to health as visceral fat.
- Visceral fat: This is the type of fat that is located deeper in the abdomen, surrounding vital organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines. Visceral fat can contribute to health problems such as insulin resistance, inflammation, and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer.
There are also different patterns of belly fat distribution:
- Apple-shaped: In this pattern, more fat is accumulated in the upper body, particularly around the waist and belly area.
- Pear-shaped: In this pattern, more fat is accumulated in the lower body, particularly around the hips and thighs.
People who have more belly fat, particularly visceral fat, are at increased risk of developing health problems. However, it’s important to remember that everyone’s body is different, and some people may carry more belly fat than others without experiencing health problems. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your belly fat or overall health.
Also Read – The Neck: Anatomy & Surgery
Importance of exercise in reducing belly fat
Exercise is an important component of Reducing belly fat, as it can help to burn Calories and improve overall health. Here are some ways in which exercise can be helpful in Reducing belly fat:
- Burns calories: Exercise can help to burn Calories and Contribute to a calorie deficit. Which is necessary for weight loss and Reducing belly fat.
- Increases metabolism: Regular exercise can help to increase Metabolism. Which can lead to increased calorie burning and greater fat loss over time.
- Reduces visceral fat: Exercise has been shown to be particularly effective in Reducing Visceral fat. Which is the type of fat that is located deep in the abdomen and is Associated with health problems.
- Improves insulin sensitivity: Exercise can help to improve insulin Sensitivity. Which is important for Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and Reducing the risk of type 2 Diabetes.
- Reduces stress: Exercise can help to reduce stress, which can Contribute to an increase in belly fat. By Reducing stress, exercise can help to improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can be helpful in Reducing belly fat and Improving overall health. Every person has a different Physique, therefore it’s important to remember that what works for one person might not work for another. Consult with a healthcare provider or Certified personal trainer to develop an exercise plan that is safe and effective for your individual needs and goals.
Hormonal changes and belly fat
Hormonal changes can Contribute to an increase in belly fat, particularly in women. Here are some of the ways in which Hormonal changes can affect belly fat:
- Menopause: Women’s Oestrogen levels fall when they go through Menopause. This can lead to an increase in belly fat, as Estrogen helps to Regulate weight distribution in the body.
- Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance, which is common in people with type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome, can lead to an increase in belly fat. Insulin resistance occurs when the body becomes less sensitive to insulin. Which can lead to an increase in blood sugar levels and an increase in the storage of fat in the belly area.
- Cortisol: Cortisol, which is often referred to as the “stress hormone”, can Contribute to an increase in belly fat. When cortisol levels are high, the body tends to store more fat in the belly area.
- Thyroid dysfunction: Thyroid dysfunction, particularly Hypothyroidism, can lead to an increase in belly fat. This is because the thyroid hormone plays an important role in Regulating Metabolism and weight.
While Hormonal changes can Contribute to an increase in belly fat, it’s important to remember that lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise also play a significant role in weight management. Consult with a Healthcare Provider if you have concerns about Hormonal changes and belly fat, and work with a registered Dietitian or Certified personal trainer to develop a plan to manage your weight and overall health.
Medical treatments for belly fat
There are a few medical treatments that may be used to target belly fat. But it’s important to note that they are typically used in conjunction with lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, rather than as a standalone solution. Here are some of the medical treatments that may be used for Visceral fat:
- Liposuction: Liposuction is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of fat from the body. It can be used to remove subcutaneous fat from the belly area. But it is not typically used for visceral fat.
- CoolSculpting: CoolSculpting is a non-invasive procedure that uses freezing temperatures to destroy fat cells. It is often used to target subcutaneous fat in the belly area.
- Bariatric surgery: Bariatric surgery is a type of weight loss surgery that is often used to treat obesity and related health problems. It may be used to reduce Visceral fat in people who are severely overweight or obese.
- Medications: There are a few medications that may be used to target Visceral fat. But they are typically used in conjunction with lifestyle changes. For example, some diabetes medications may help to reduce belly fat in people with insulin resistance.
It’s important to remember that medical treatments for belly fat should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, and that lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise are typically the first line of defense against belly fat and related health problems.
Importance of maintaining a healthy weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for overall health and can help to reduce the risk of many chronic diseases. Here are some of the factors that make it crucial to maintain a healthy weight:
- Reduces the risk of chronic diseases: Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the risk of many chronic diseases. Including heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis.
- Improves mental health: Being overweight or obese can contribute to poor mental health, including depression and anxiety. Maintaining a healthy weight can help to improve mood and overall mental health.
- Increases energy levels: Carrying excess weight can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks and lead to feelings of fatigue. Maintaining a healthy weight can help to increase energy levels and improve overall quality of life.
- Improves sleep: Being overweight or obese can contribute to sleep apnea and other sleep disorders. Maintaining a healthy weight can help to improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of sleep disorders.
- Boosts self-esteem: Maintaining a healthy weight can help to boost self-esteem and confidence. Which can lead to a more positive outlook on life.
It’s important to remember that maintaining a healthy weight is not just about physical appearance. But is also crucial for overall health and well-being. A healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help to develop a plan for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight that is safe and effective for your individual needs and goals.
Tracking progress
Tracking progress is an important part of achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Here are some pointers for monitoring development:
- Set specific goals: Setting precise, quantifiable objectives can help you stay focused and on course. For example, you may set a goal to lose a certain amount of weight, to exercise a certain number of days per week, or to reduce your intake of sugary foods.
- Keep a food diary: Keeping a food diary can help to track your calorie intake and identify areas where you may be able to make healthier choices. There are many apps and websites that can help you track your food intake and provide feedback on your nutrient intake.
- Take measurements: Taking measurements such as waist circumference, body mass index (BMI), and body fat percentage can help to track changes in body composition over time.
- Monitor physical activity: Keeping track of your physical activity can help you to monitor progress and make adjustments to your routine as needed. You may use a fitness tracker or pedometer to monitor your steps or use an app to track your workouts.
- Celebrate progress: Celebrating progress, even small milestones, can help to keep you motivated and on track. This could include treating yourself to a new workout outfit or a healthy meal at your favorite restaurant.
Be patient and persistent because progress takes time. It’s crucial to put more emphasis on general health and wellbeing than just weight loss. A healthcare provider or registered dietitian can provide guidance on setting realistic goals and tracking progress in a safe and effective way.
Also Read – Calorie: How Many Should You Consume Each Day?
The function of stress in the development of abdominal fat
Stress can play a role in belly fat accumulation. When you experience stress, your body releases a hormone called cortisol. Which can increase appetite and promote the storage of fat, particularly in the abdominal area.
In addition, stress can also lead to unhealthy coping behaviors, such as overeating or turning to comfort foods. Which can contribute to weight gain and belly fat accumulation.
Chronic stress can be particularly problematic, as prolonged exposure to cortisol can lead to insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other chronic diseases.
While it’s not always possible to eliminate stress from our lives, there are strategies that can help to manage stress and reduce its impact on belly fat accumulation. These strategies may include:
- Engaging in relaxation routines like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, which can help to reduce stress levels and promote weight loss.
- Getting adequate sleep, as lack of sleep can increase cortisol levels and lead to increased appetite and belly fat accumulation.
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats.
- Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional. As social support can help to reduce stress levels and promote healthy behaviors.
It’s important to remember that managing stress and reducing belly fat accumulation requires a holistic approach that takes into account many different factors. Including diet, physical activity, sleep, and mental health. A healthcare provider or registered dietitian can provide guidance on developing a comprehensive plan for managing stress and reducing Visceral fat accumulation in a safe and effective way.
The impact of sleep on belly fat
Sleep plays an important role in many aspects of health, including weight management and belly fat accumulation. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism. Leading to increased appetite, decreased physical activity, and weight gain, including the accumulation of Visceral fat.
Here are some ways that sleep can impact belly fat:
- Hormonal imbalances: Lack of sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances that increase appetite and promote fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area. For example, lack of sleep can lead to increased levels of the hormone ghrelin. Which stimulates appetite, and decreased levels of the hormone leptin, which signals fullness.
- Decreased physical activity: Lack of sleep can also lead to decreased physical activity. As tiredness can make it more difficult to engage in exercise or other physical activities.
- Unhealthy food choices: Lack of sleep can also lead to increased cravings for unhealthy, high-calorie foods that can contribute to weight gain and belly fat accumulation.
- Insulin resistance: Lack of sleep can also lead to insulin resistance. Which can make it more difficult for the body to regulate blood sugar levels and can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Getting adequate sleep is important for overall health, including maintaining a healthy weight and reducing belly fat. The Adults should strive for 7-9 hours of sleep each night, according to the National Sleep Foundation. If you have difficulty sleeping, there are strategies that can help. Such as establishing a regular sleep routine, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and creating a sleep-conducive environment in your bedroom. If you continue to have difficulty sleeping, it may be helpful to speak with a healthcare provider or sleep specialist.
The importance of resistance training
Resistance training, also known as strength training or weight lifting, can play an important role in reducing belly fat and improving overall health. Here are some ways that resistance training can impact belly fat:
- Increased muscle mass: Resistance training can help to increase muscle mass, which can boost metabolism and promote weight loss. Muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat tissue. So increasing muscle mass can help to burn more calories at rest and during physical activity.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Resistance training can also improve insulin sensitivity. Which can help to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is particularly important for reducing belly fat, as insulin resistance is associated with increased abdominal fat accumulation.
- Reduced inflammation: Resistance training can also reduce inflammation in the body. Which is associated with a higher risk of chronic diseases, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
- Increased fat burning: Resistance training can also help to increase fat burning, particularly when combined with aerobic exercise. This may result in less body fat overall, including less belly fat.
Incorporating resistance training into your exercise routine can be a valuable tool for reducing belly fat and improving overall health. It’s important to start slowly and work with a qualified fitness professional to ensure that you are using proper form and technique to avoid injury. Resistance training can be done using free weights, resistance bands, weight machines, or bodyweight exercises, and should be done 2-3 times per week, with a focus on targeting all major muscle groups.
The impact of alcohol on belly fat
Consuming alcohol in excess can contribute to the accumulation of belly fat. Here are some ways that alcohol can impact belly fat:
- Increased calorie intake: Alcoholic beverages can be high in calories, and drinking can lead to increased calorie intake. Excess calories are stored as fat, particularly around the abdominal area.
- Disrupted metabolism: Alcohol consumption can disrupt the body’s metabolism and contribute to the storage of fat in the abdominal area.
- Increased appetite: Drinking alcohol can also increase appetite and lead to overeating or making poor food choices। hich can contribute to weight gain and belly fat accumulation.
- Hormonal changes: Excess alcohol consumption can disrupt the balance of hormones in the body, which can lead to increased fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area.
If you are trying to reduce belly fat, it is important to moderate your alcohol consumption. Men should restrict their alcohol consumption to two drinks per day. While women should limit their consumption to one drink per day, according to the American Heart Association. In addition, choosing lower calorie options, such as light beer or wine, can help to reduce calorie intake. It’s also important to be mindful of the amount of added sugar in mixers. As these can also contribute to weight gain and belly fat accumulation.
Sustainable lifestyle changes for long-term success
To achieve long-term success in reducing belly fat, it is important to make sustainable lifestyle changes that you can maintain over time. Here are some pointers for implementing long-lasting changes:
- Set realistic goals: It’s important to set goals that are realistic and achievable, and to be patient with the process. Rapid weight loss is often not sustainable and can lead to regain over time.
- Make gradual changes: Instead of making drastic changes to your diet or exercise routine, start by making small, gradual changes that you can maintain over time. For example, try adding one serving of vegetables to your meals each day or going for a 10-minute walk after dinner.
- Focus on overall health: Instead of just focusing on weight loss or belly fat reduction, focus on improving your overall health. This includes eating a balanced diet, getting regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting enough sleep.
- Find activities you enjoy: Physical activity should be enjoyable and sustainable. So find activities that you enjoy and that fit into your lifestyle. This could be anything from walking or cycling to dancing or swimming.
- Seek support: Having social support can be a valuable tool for making sustainable changes. This could include working with a registered dietitian or personal trainer, joining a fitness class, or finding a workout buddy.
By making sustainable lifestyle changes, you can achieve long-term success in reducing Visceral fat and improving your overall health. Remember to be patient with the process and to focus on overall health rather than just weight loss.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is provided for Informational reasons and is not meant to be personal medical advice. You should consult your doctor or another Qualified fitness professional if you have any concerns about a Systemic condition. Never Disregard professional medical advice or give up looking for it because of something you read on this website. The Daddydontblog.com does not promote or recommend any products.






Wow, amazing blog format! How long have you ever been running a blog for?
you made blogging glance easy. The overall look of
your web site is fantastic, as smartly as the content material!
You can see similar: sklep internetowy and here dobry sklep